Introduction And Who Might Need This
- ourservices
WHAT IS IN VITRO FERTILIZAITON
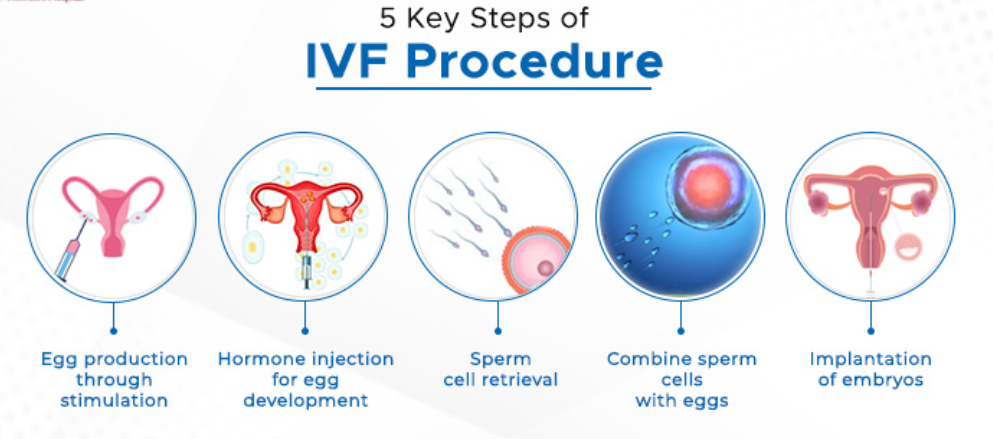
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a type of assisted reproductive technology (ART) where sperm and an egg are fertilized outside of the human body. IVF is a complex process that involves retrieving eggs from ovaries and manually combining them with sperm in a lab for fertilization. Several days after fertilization, the fertilized egg (now called an embryo) is placed inside a uterus. Pregnancy occurs when this embryo implants itself into the uterine wall.
WHY IS IVF PERFORMED
Sometimes, IVF is offered as a main treatment for infertility in people over the age of 40. It also can be done if you have certain health conditions. For example, IVF may be an option if you or your partner has:
· Fallopian tube damage or blockage. Eggs move from the ovaries to the uterus through the fallopian tubes. If both tubes get damaged or blocked, that makes it hard for an egg to be fertilized or for an embryo to travel to the uterus.
· Ovulation disorders. If ovulation doesn’t happen or doesn’t occur often, fewer eggs are available to be fertilized by sperm.
· Endometriosis. This condition happens when tissue that’s like the lining of the uterus grows outside of the uterus. Endometriosis often affects the ovaries, uterus and fallopian tubes.
· Uterine fibroids. Fibroids are tumors in the uterus. Most often, they’re not cancer. They’re common in people in their 30s and 40s. Fibroids can cause a fertilized egg to have trouble attaching to the lining of the uterus.
· Previous surgery to prevent pregnancy. An operation called tubal ligation involves having the fallopian tubes cut or blocked to prevent pregnancy for good. If you wish to conceive after tubal ligation, IVF may help. It might be an option if you don’t want or can’t get surgery to reverse tubal ligation.
· Issues with sperm. A low number of sperm or unusual changes in their movement, size or shape can make it hard for sperm to fertilize an egg. If medical tests find issues with sperm, a visit to an infertility specialist might be needed to see if there are treatable problems or other health concerns.
· Unexplained infertility. This is when tests can’t find the reason for someone’s infertility.
· A genetic disorder. If you or your partner is at risk of passing on a genetic disorder to your child, your health care team might recommend getting a procedure that involves IVF. It’s called preimplantation genetic testing. After the eggs are harvested and fertilized, they’re checked for certain genetic problems. Still, not all of these disorders can be found. Embryos that don’t appear to contain a genetic problem can be placed in the uterus.
· A desire to preserve fertility due to cancer or other health conditions. Cancer treatments such as radiation or chemotherapy can harm fertility. If you’re about to start treatment for cancer, IVF could be a way to still have a baby in the future. Eggs can be harvested from their ovaries and frozen for later use. Or the eggs can be fertilized and frozen as embryos for future use.
People who don’t have a working uterus or for whom pregnancy poses a serious health risk might choose IVF using another person to carry the pregnancy. The person is called a gestational carrier. In this case, your eggs are fertilized with sperm, but the embryos that result are placed in the gestational carrier’s uterus.